Eshealthtips.com – Diabetes skin lesions are a common complication, with the most common presentation being hyperpigmented patches on the legs. Although the condition is typically benign, the lesions may itch, blister, or appear shiny. Diabetic skin lesions may also respond to trauma. Patients with the condition often seek treatment for the condition in an effort to reduce their appearance and alleviate the discomfort. This article will explore the causes and symptoms of diabetic skin lesions.
Diabetic Skin Lesions are Higher in Women
In this study, the prevalence of diabetes-related skin lesions was higher among women than in men. This may reflect the greater health concerns of women with diabetes. In addition, the prevalence of skin manifestations increased with the duration of diabetes, with a higher rate of lesions reported among women with T2DM than in Type 1 diabetics. However, these findings should be interpreted with caution. The researchers suggest that there may be an underdiagnosed cause of the lesions.
Diabetes-related skin lesions may be a sign of metabolic syndrome, a syndrome characterized by elevated insulin levels. This condition is also known as syndrome X. Symptoms in this disorder include dark pigmentation and velvety texture on the skin. The condition is also often accompanied by other medical conditions, such as obesity. In this condition, the patient may require insulin therapy. Symptomatic treatment will depend on whether the lesions are caused by diabetes.
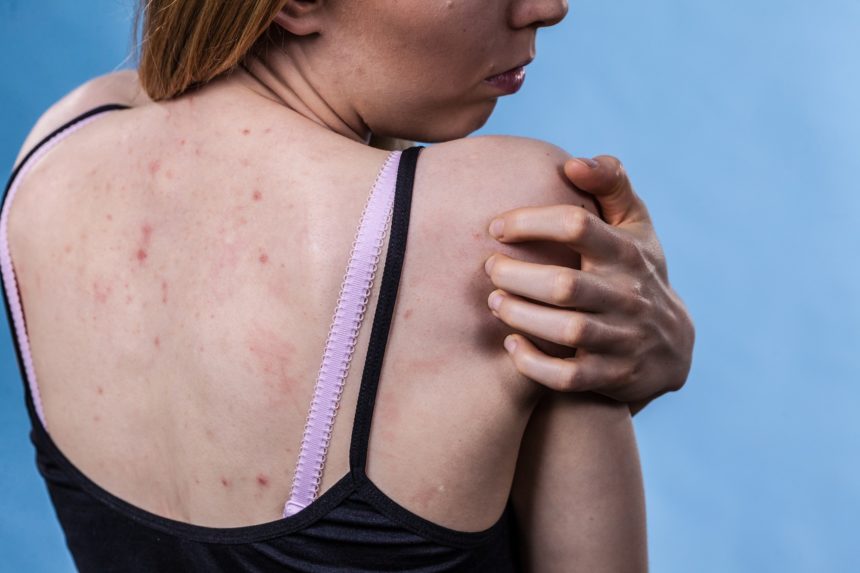
Another common skin symptom of diabetes is chronic pruritus, which often occurs in conjunction with xerosis cutis. Diabetic polyneuropathy may also have an impact on the patient’s ability to sweat because of damaged sympathetic nerves. Xerosis, a type of dermatitis, is caused by an abnormal persistent cohesion between the corneocytes of the stratum corneum (SC). This condition leads to increased thickness of the upper layers of SC, and it may also be linked to microangiopathy.
Common Symptoms of Diabetic Skin Disease
Some common symptoms of diabetic skin disease include pink, tanned, and dark brown patches. The patches are flat, oval, or round, and may even be affixed with nodules. These lesions aren’t painful, and may appear similar to age spots. The affected area is most often the lower legs, but they can also occur on the face, forearms, front of the thighs, or trunk.
A systematic review was conducted to determine the prevalence of diabetic skin lesions. Specifically, articles related to this topic were found in the Iranian Medex, IranDoc, and MagIran databases. Relevant articles were also included in the Google Scholar database and in the Cochrane database without a lower time limit. Finally, the databases ScienceDirect, Scopus, PubMed, and Web of Science were used to examine the prevalence of skin lesions among diabetic patients.
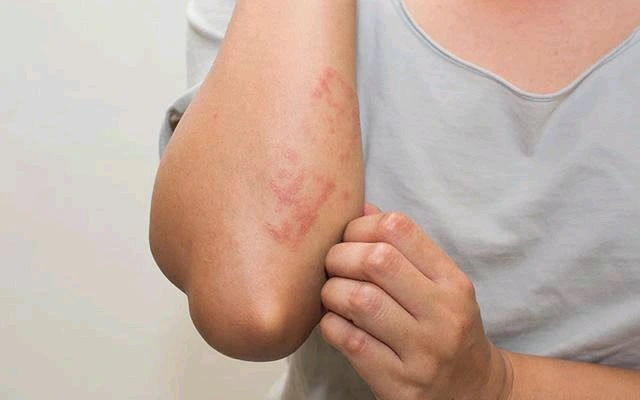
Some of the most common skin lesions associated with diabetes are caused by hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar. High blood sugar causes the body to pull fluid from other cells, causing dry skin, which is also known as xerosis. Diabetic neuropathy, or nerve damage, is another cause of dry skin. Diabetic skin lesions should be addressed as soon as possible, as they can lead to other health complications.
Proper Diabetic Skin Care
Managing the blood sugar level can prevent the formation of diabetic skin lesions. Keeping blood glucose levels within the recommended ranges is a great way to prevent these conditions and slow the rate at which they occur. Diabetic dermopathy is more common on the legs and shins than other areas of the body. It’s important to follow your doctor’s recommendations regarding proper diabetic skin care and controlling blood sugar levels.
Treatment for diabetic skin lesions depends on their severity. Early treatment can improve prognoses, prevent health consequences, and reduce the cost of complications. In the case of diabetic skin ulcers, early intervention is crucial. Diabetic skin ulcers may require surgical procedures. While debridement and dressing change therapy may provide some relief in the short term, if left untreated, they can lead to amputation.
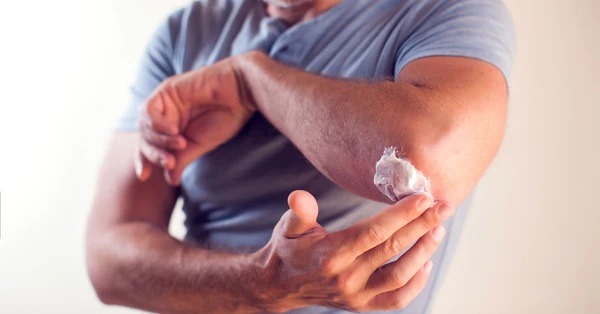
Acute and chronic wounds are common complications of diabetes. Diabetic patients may suffer from neuropathy, a condition that damages the nerves of the skin. As a result, they are susceptible to repeated injuries and infections. Also, vascular disease can reduce the blood flow to the skin, cutting off vital nutrients and oxygen that are needed for healthy tissue healing. In addition to this, 19 to 34 percent of patients with diabetes will develop chronic foot ulcers, which are extremely painful. If these ulcers are untreated, they can lead to death. If you wish to send your article to eshealthtips, you can check out this page!