Eshealthtips.com – When a wound begins to bleed, you will notice serious drainage. This watery substance is similar to blood plasma and can be a sign of a more serious complication. Serous drainage is not always harmful, and you may be able to handle the bleeding on your own. However, it is important to consult a doctor if you notice it increasing or changing. In some cases, this fluid may lead to an infection.
Watery and Pale Yellow Serous Drainage
In some cases, serous drainage is watery and pale yellow. This type of fluid is common in partial-thickness wounds and venous ulcers. The serum is normally clear, but a few cells of blood may be present in it. In addition, it is common for serious fluid to contain tiny red blood cells. If you notice the drainage is changing color, then you may have a wound infection.
There are several different types of wound drainage, but the most common is serosanguineous. It is clear to pink and contains small amounts of red blood cells. It is normal to have some serosanguineous fluid, and it usually occurs during the inflammatory stage of the wound healing process. When you have large amounts of serosanguinous drainage, however, you should visit your doctor to find out if there is a serious underlying wound infection.
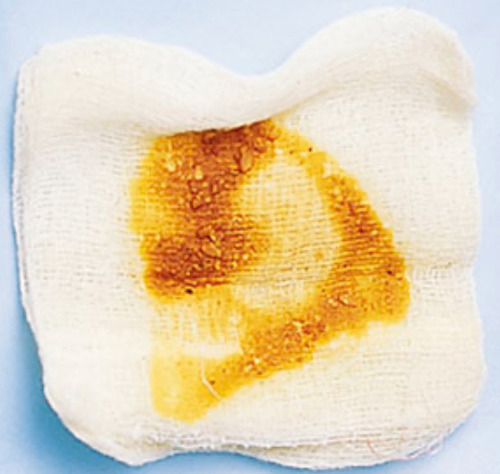
Usually, serosanguineous fluid presents itself during the inflammatory stage of wound healing. Serosanguineous fluid is released by damaged cells to attract immune cells. When this fluid is present in small amounts, it is not a cause for concern. It may be a sign of active bleeding. This discharge is normal and usually lasts for a few days. Serous fluid may stick to dressings, which can damage capillaries and lead to further complications.
Types of Drainage and Symptoms Cause
A discharge that is thick, milky, or purulent contains bacteria and microorganisms. It is also sometimes tinged with white blood cells and may be a sign of infection. In addition to a clear, pink or white discharge, it may also contain pus. The amount of drainage depends on the underlying infection, but it is usually minimal, moderate, or large. Your doctor can determine what is causing the drainage if you have these symptoms.
In case you’ve had an injury that requires medical attention, you may notice a thin, milk-like liquid that is emitted from the wound. Serosanguineous drainage is a normal part of the healing process. If it becomes excessive, however, it is a sign of a more serious complication. If you see this type of fluid, see a doctor immediately. This type of drainage is not normal, and is a strong sign of infection. Regardless of the cause, it’s important to consult with your doctor if you have noticed any unusual or persistent drainage from your wound.
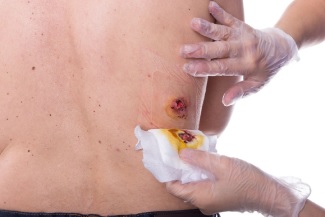
If you notice pink serous drainage from a wound, don’t worry! It’s common in the early stages of wound healing and is a symptom of infection and slow healing. If it persists, seek medical attention right away, as it is a sign of a more serious infection. You may also need antibiotic treatment. But for now, your doctor will be able to give you more specific instructions on the proper treatment for your particular wound.
The Most Common Drainage Characteristics
The most common type of drainage is serosanguineous, which is thin, watery, and pink. Sometimes, this drainage may be a darker red color. In either case, the blood cells are a sign of capillary damage. The doctor will look closely at the color, texture, and quantity of the drainage. If the exudate does not reach 25% of the dressing, then the wound is not a significant source of infection.
In most cases, persistent wound drainage stops within two to four days, but it can be long-term. In patients with persistent wound drainage, the initial treatment includes incisional NPWT and compression wrapping with hip spica dressing. In some cases, surgical irrigation and debridement is required, but this is not a definite cure for persistent wound drainage. Patients may need a biopsy to rule out other causes of persistent seroma.
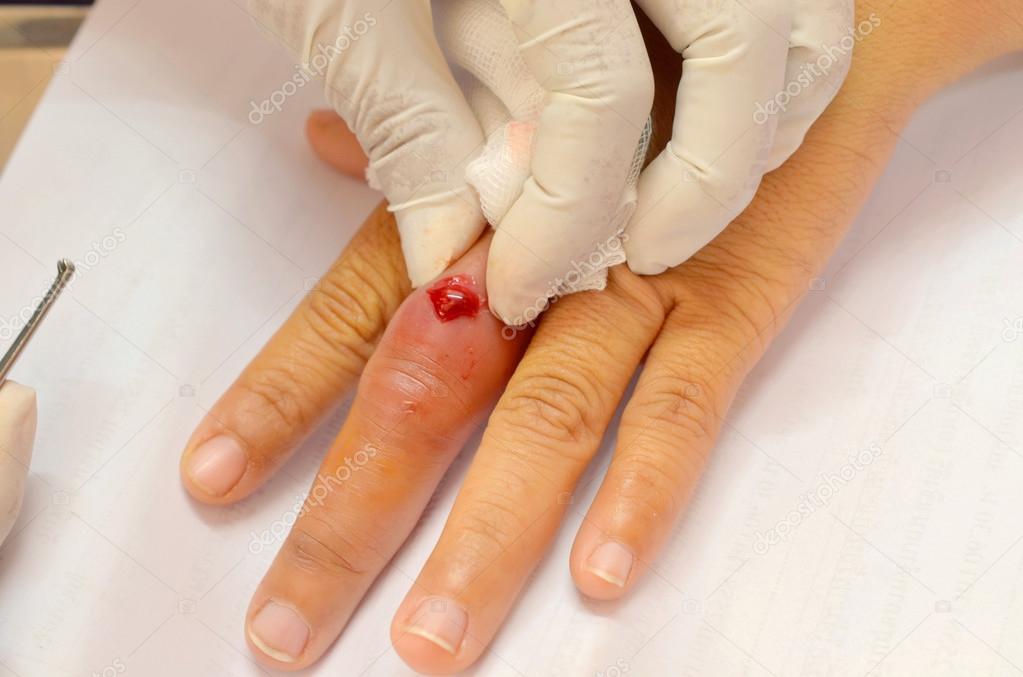
If you notice a strange odor coming from your wound, it may be a sign of an infection. In such cases, you should consult a doctor to determine the cause and the appropriate treatment. Proper wound care can prevent infections and speed the recovery process. Ensure that you wash your hands thoroughly before dressing a wound, and change your bandages regularly. If you notice any of these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
Reference: