Eshealthtips.com – The Descending Aorta (DA) is the main artery in the thorax and abdomen. It gives off nine pairs of posterior intercostal arteries, two subcostal arteries, two bronchial arteries to the left lung, and a small branch to the oesophagus. Depending on the specific aneurysm, it may be partially or fully dissected. In rare cases, it may be double, in which case the aorta opens into the aneurism and looks like a proper blood vessel.
Descending Aortic Graft
The Descending Aorta is a long artery that runs through the posterior center of the trunk. It passes through the lungs and esophagus before entering the abdominal cavity. It is also a major source of compression of the bronchial artery. The surgical procedure aimed to relieve the bronchial pressure and remove the vascular ring is called a descending aorta graft (DAT).
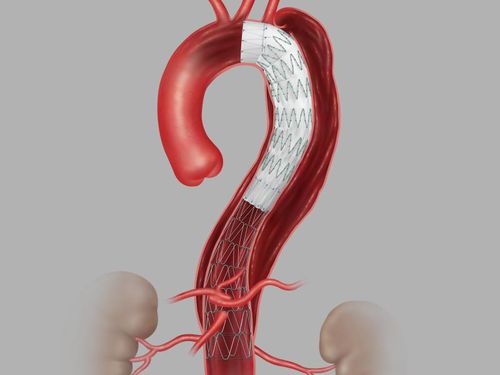 The Descending Aorta is a large blood vessel that starts after the left subclavian artery and runs to the diaphragm. This blood vessel supplies important blood flow to the spinal cord and is more amenable to endovascular approaches, but open surgery is still necessary for complex cases. When aneurysm occurs in the Descending Aorta, it is called a thoracoaortic aneurysm.
The Descending Aorta is a large blood vessel that starts after the left subclavian artery and runs to the diaphragm. This blood vessel supplies important blood flow to the spinal cord and is more amenable to endovascular approaches, but open surgery is still necessary for complex cases. When aneurysm occurs in the Descending Aorta, it is called a thoracoaortic aneurysm.
The Descending Aorta is the most common source of aortic dissection in adults. It starts in the abdominal cavity and extends down the posterior center of the trunk. It also travels past the heart and lungs before reaching the esophagus. Once in the abdominal cavity, the descending Aorta enters the bloodstream. This area is referred to as the aortic arch.
Largest Blood Vessel in the Body
The descending aorta is the first section of the aorta. It is the largest blood vessel in the body and helps the heart to deliver oxygen-rich blood throughout the body. However, the aorta can rupture at any time, and can be life-threatening. It is important to consult your healthcare provider and take precautions to minimize your risk of developing a ruptured aneurysm.
The pain associated with Descending Aorta is usually located in the thorax and back. The dissection may cause bleeding and uncontrolled hypertension. It can also cause paraplegia, which can lead to death. Fortunately, the descending aorta can be treated medically. Patients can avoid surgery, as it involves a traumatic experience for the aortic arch.
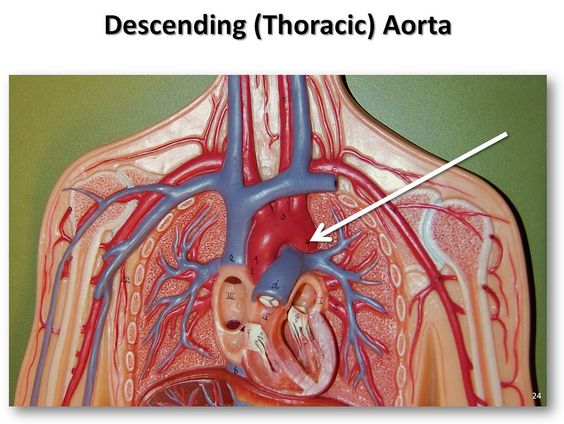 The Descending Aorta is the first section of the aorta and the largest blood vessel in the body. It is responsible for delivering oxygen-rich blood to the heart and other parts of the body. The aorta is an important part of the heart and should be looked after carefully. If it is damaged, it can cause significant airway compression. If left, the aorta crosses the midline to the right, the aorta becomes a ‘ring’.
The Descending Aorta is the first section of the aorta and the largest blood vessel in the body. It is responsible for delivering oxygen-rich blood to the heart and other parts of the body. The aorta is an important part of the heart and should be looked after carefully. If it is damaged, it can cause significant airway compression. If left, the aorta crosses the midline to the right, the aorta becomes a ‘ring’.
Aortic Surgery is Less Invasive Than Other Areas of the Body
The descending aorta begins below the left subclavian artery and continues down the diaphragm. It is important for the circulation of blood in the thorax and spinal cord. Aorta surgery is less invasive than surgery on other areas of the body. It is often associated with a decreased risk of stroke. It can also result in lower-limb amputation.
The Descending Aorta is the aortic arch of the heart. It runs from the left aortic arch to the right. The descending aorta passes through the diaphragm and enters the abdominal cavity. When this happens, the aorta can rupture and lead to amputation. The aorta is divided into four parts.
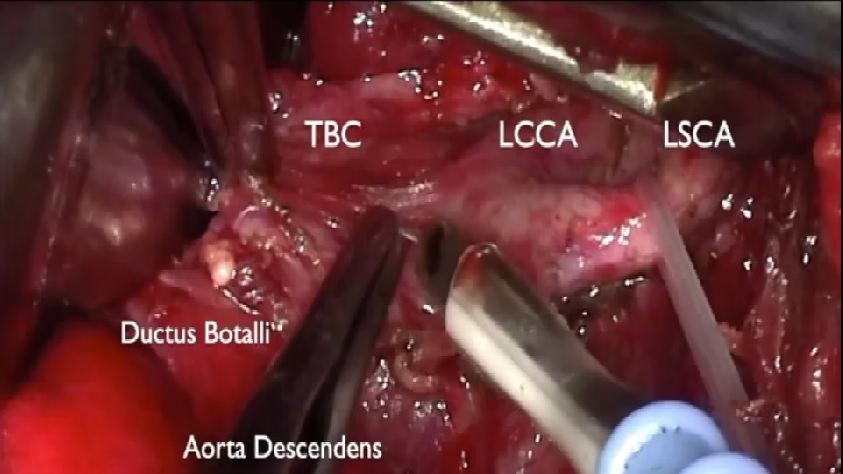
The Descending Aorta is the most common aortic branch. It is found at the lower border of the T4 vertebra. It branches off from the coronary arteries. The descending aorta continues to travel through the thoracic cavity. As it descends, it leaves the posterior mediastinum and becomes the abdominal aorta. It is attached to the ribs and other chest structures.
Reference: